Biodiversity Hotspots in Conservation
What is biodiversity?
- Biodiversity is the variety of life on earth. Biodiversity is most simply thought of as the number of species found on earth, or in a given area.
Why is biodiversity important?
- All organisms have a role in ecosystems. If a species is removed, the important function they have in an ecosystem is lost.
- If diversity is high, it is more likely that there is another species in an ecosystem that can perform that function. This means that diversity generally increases the stability or resilience of an ecosystem.
- Resilience can be defined as the ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbance, or a change in the ecosystem.
- Biological organisms and the roles they play in ecosystems result in the provision of ecosystem services to humans. Ecosystem services are defined as the benefits that humans derive from natural ecosystems. These can include products such as medicines or food and processes such as shoreline stabilization, purification of air and water, carbon sequestration, and seed dispersal. Ecosystems can also provide non-material services to humans such as recreation and inspiration.
- The loss of biodiversity can mean a loss of these important ecosystem services.
Conservation
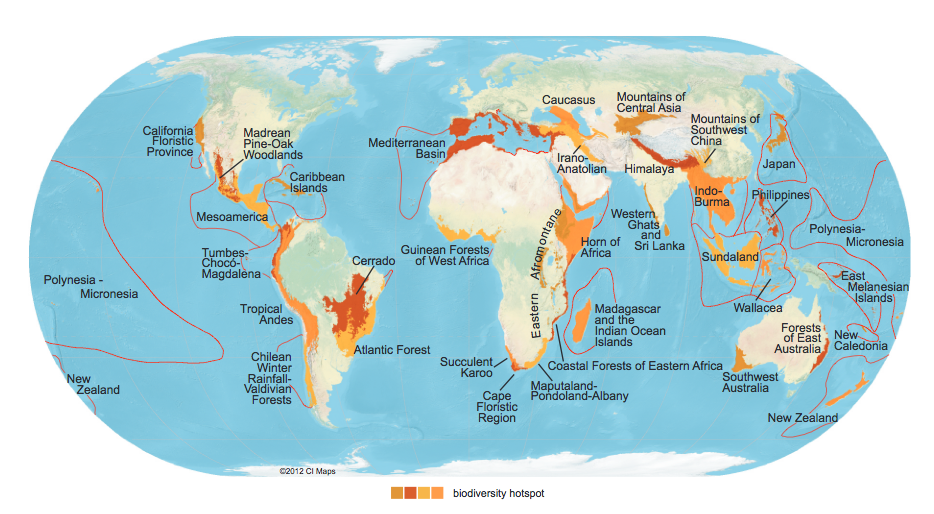
- Biodiversity hotspot is a term used in conservation to refer to an area with high biological diversity that is threatened by human activities (www.conservationinternational.org).
- The term biodiversity hotspot is different than the terms diversity and species hotspots that we have been using in Ocean Tracks. Biodiversity hotspots have a specific definition that was created by scientists and conservationists for conservation purposes (see below). The hotspot terms we’re using in Ocean Tracks more generally refer to important habitat areas for the four Ocean Tracks species in the ocean.
- Scientists have specific criteria for an area to qualify as a biodiversity hotspot. The area must have a certain number of species that are unique to that particular area (known as endemic, or found nowhere else in the world), and this area has to have lost more than 70% of it’s original habitat area (Myers 2000).
- Defining areas as biodiversity hotspots is done as a way of prioritizing money put towards conservation. The idea is that spending money to protect these areas has the highest positive outcome for a given amount of money.
- There are 34 biological hotspots across the globe, shown below.
Back to Top

